|
|
Profile
|
Delegates :
Masayuki Aso |
|
Incorporated :
October 20 , 2003 |
Paid in Capital :
439 Million yen |
Employees :
16 人 |
Address :
Chiba-dai Inohana Innovation Plaza 1-8-15, Inohana, Chuo-ku,Chiba-city CHIBA
〒260-0856
|
TEL/FAX :
+81-43-441-4121 / +81-43-441-4121 |
URL:
http://www.cellgentech.com/english/e_index.html |
Attachment :
|
Mission/Background :
CellGenTech is a bio-venture company in close collaboration with Chiba University. The company seeks to develop regenerative medicine treatments to patients suffering from congenital genetic deficiency diseases, by providing genetically modified adipocytes. CellGenTech dedicates to improve the quality of life of patients suffering from various refractory diseases through providing therapeutically useful gene transduced adipocytes. |
|
Technology & Business
|
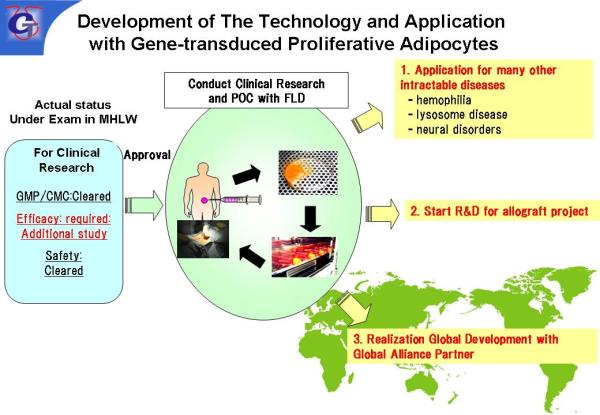
As a venture company from Chiba University, we are working on the research and development of genetically modified adipocytes (hereinafter referred to as “GMAC”) using human adipocytes. Our strategy for the replacement therapy of deficient protein or enzyme is to develop the breakthrough GMAC which possess the ability to continuously secret the required protein or enzyme for a long period of time by transfecting the requisite gene to autologous adipocytes.
Transplanting GMAC to patients who are deficient in proteins and enzymes due to refractory genetic diseases or lifestyle- and aging-related change, the burden on hospital treatment will be greatly reduced, and the QOL of patients and their families will be improved dramatically.
Adipocytes used for the preparation of GMAC are one of excellent secretory cells. This characteristic aspect makes itself a generally applicable gene therapy platform technology that can treat any intractable diseases by changing the gene transfected.
|
|
Products & Service
|
Products & Service Name
|
Stage
|
Outline
|
Milestone
|
GMAC for the treatment of familial LCAT deficiency
|
Preclinical
|
LCAT gene transfected GMAC that enables stable and long-term supply of LCAT for familial LCAT deficiency.
|
To conduct the clinical trial (under preparation of clinical trial application)
|
Transgenic GMAC to replace therapeutic proteins for the treatment of lysosomal disease (e.g. Fabry disease) and hemophilia.
|
Discovery
|
Confirmed the feasibility studies of GMACs for lysosome disease and hemophilia as a commissioned project of JST.
|
Joint research and joint development with alliance partners
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Highlights
|
Familial LCAT deficiency is a rare disease in which lecitin cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT), which increases good cholesterol, and has outcomes on damages of the eyes and kidneys. In collaboration with Chiba University, LCAT gene-transfected GMAC has been proven enabled successful supplementation of LCAT. We conducted the world's first clinical study using the patient's own adipocytes. A single GMAC administration has shown the lipid metabolism improvement for over 2 years.
|
|
Hot news
|
Adopted by Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development as a basic technology development project for the industrialization of regenerative medicine (from October 2018 to March 2020, total subsidy of approximately 91 million yen). From 2018 to 2019, we have raised approximately 800 million yen through third-party allotment for operating companies and venture capitals to accelerate research and development.
|
|
Alliance strategy
|
GMAC is expected to treat congenital metabolic abnormality by improving protein / enzyme deficiency disorders, and treatment of refractory chronic diseases by recombinant protein secretion to correct the pathology.
Our mission is to provide versatile GMAC to patients suffering from any intractable diseases. We are looking forward to receiving contact from pharmaceutical companies, life science companies and research institutions interested in this technology.
|
|
|